Teach AQA module AB: Germany, 1890-1945: Democracy and dictatorship, no prep needed!
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be fully prepared to teach any AQA GCSE topic?
Every AQA topic is covered, and each module comes complete with:
AB Germany, 1890-1945: Democracy and Dictatorship
This module focuses on the development of Germany at the turn of the 20th century. It explores the turbulent period of change from democracy during the Weimar Republic era to that of dictatorship during the rise to power and eventual fall of Nazism. Topics covered include the political, economic and cultural environments and their aspects under the two different political systems. Key individuals and policies are also examined to frame and contextualise the changes that occurred.
The module is divided into three parts, which are detailed below and are aligned with the specifications of the AQA handbook.
Part one: Germany and the growth of democracy
Themes covered include:
- Kaiser Wilhelm II and the difficulties of ruling Germany: the growth of parliamentary government; the influence of Prussian militarism; industrialisation; social reform and the growth of socialism; the domestic importance of the Navy Laws.
- The impact of WWI: war weariness, economic problems; defeat; the end of the monarchy; post-war problems including reparations, the occupation of the Ruhr and hyperinflation.
- Weimar democracy: political change and unrest, 1919–1923, including Spartacists, Kapp Putsch and the Munich Putsch; the extent of recovery during the Stresemann era (1924–1929): economic developments including the new currency, Dawes Plan and the Young Plan; the impact of international agreements on recovery; Weimar culture.
Part two: Germany and the Depression
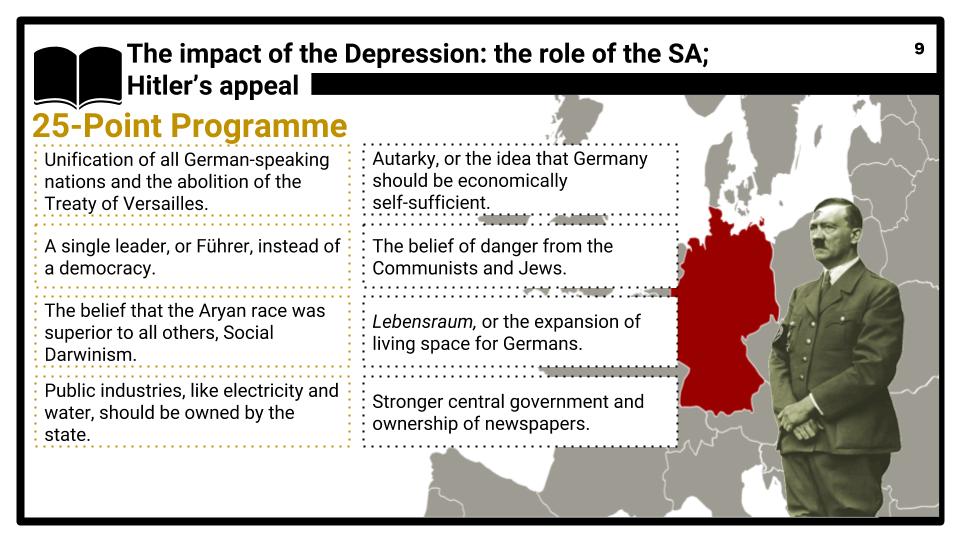
- The impact of the Depression: growth in support for the Nazis and other extremist parties (1928–1932), including the role of the SA; Hitler’s appeal.
- The failure of Weimar democracy: election results; the role of Papen and Hindenburg and Hitler’s appointment as Chancellor.
- The establishment of Hitler’s dictatorship: the Reichstag Fire; the Enabling Act; elimination of political opposition; trade unions; Rohm and the Night of the Long Knives; Hitler becomes Führer.
Part three: The experiences of Germans under the Nazis
- Economic changes: benefits and drawbacks; employment; public works programmes; rearmament; self-sufficiency; the impact of war on the economy and the German people, including bombing, rationing, labour shortages, refugees.
- Social policy and practice: reasons for policies, practices and their impact on women, young people and youth groups; education; control of churches and religion; Aryan ideas, racial policy and persecution; the Final Solution.
- Control: Goebbels, the use of propaganda and censorship; Nazi culture; repression and the police state and the roles of Himmler, the SS and Gestapo; opposition and resistance, including White Rose group, Swing Youth, Edelweiss Pirates and July 1944 bomb plot.
Each module is accompanied by three evaluation assignments and a homework assignment as well as an assessment quiz and answer sheet.
This module download also includes the following teaching resources:
- L8 Social Darwinism And The Nazis (pdf)
- L8 Nazi Germany Mark Scheme (pdf)
- L8 Women In Germany Statistics (pdf)
- L8 Nazi Germany Mark Scheme (doc)
- L8 Life In Nazi Germany Homework (pdf)
- L6 How Hitler Became Chancellor In 1933 (pdf)
- L9 The Role Of The Ss (pdf)
- L4 Hitler And Mein Kampf Info (pdf)
- L4 Hitler Facebook Homework (pdf)
- L4 Hitler And Mein Kampf (pdf)
- L4 Hitler And Mein Kampf Info (doc)
- L8 Persecution Of The Minorities (pdf)
- L5 Consequences Of The Munich Putsch Blank Diagram (pdf)
- L8 Social Darwinism And The Nazis (doc)
- L8 Concentration And Death Camps (pdf)
- L3 Stresemann S Strategies Information (docx)
- L8 Nazi Policies Towards German Youth (pdf)
- L4 Nazi Party Reorganisation (pdf)
- L8 Life In Nazi Germany Homework (docx)
- L4 Nazi Party Reorganisation (docx)
- L7 Employment And Living Standard Information Gathering Sheet (pdf)
- L5 Consequences Of The Munich Putsch Blank Diagram (docx)
- L4 Hitler Facebook Homework (ppt)
- L8 Women In Germany Statistics (doc)
- L7 Employment And Living Standards (docx)
- L9 The Role Of The Ss (doc)
- L3 Stresemann S Strategies Information (pdf)
- L7 Employment And Living Standard Information Gathering Sheet 2 (docx)
- L7 Employment And Living Standards (pdf)
- L7 Employment And Living Standard Information Gathering Sheet (docx)
- L3 Art And Culture (docx)
- L8 Concentration And Death Camps (doc)
- L8 Nazi Policies Towards German Youth (docx)
- L9 Martin Niemoller (mp4)
- L3 Stresemann S Strategies (docx)
- L8 Persecution Of The Minorities (doc)
- L4 Sa Source Work (doc)
- L4 Hitler And Mein Kampf (doc)
- L3 Art And Culture (pdf)
- L6 How Hitler Became Chancellor In 1933 (doc)
- L4 Reasons Why The Nazi Party Grew In Popularity 1929-32 (pdf)
- L2 Homework 1 (pdf)
- L6 Hitler S Rise After The Reichstag Fire (mp4)
- L4 Appeal Fill In The Blanks Sheet (pdf)
- L6 Night Of The Long Knives The 20th Century World History Khan Academy (mp4)
- L9 The Swing Youth Movement In Nazi Germany (mp4)
- L4 Growth Of Nazi Party Popularity Wall Information (pdf)
- L4 Adolf Hitler Timeline (pdf)
- L6 Night Of The Long Knives (pdf)
- L3 Stresemann S Strategies (pdf)
- L2 The German Revolution (docx)
- L4 Sa Source Work (pdf)
- L9 The White Rose Movement (mp4)
- L8 Nazi Policies Towards Women (mp4)
- L2 Weimar Republic Constitution Diagram (pdf)
- L6 Night Of The Long Knives (docx)
- L2 Impact Of The Treaty Of Versailles (pdf)
- L9 The Edelweiss Pirates (mp4)
- L4 Appeal Fill In The Blanks Sheet (doc)
- L2 Weimar Republic Constitution Diagram (pptx)
- L5 How Did Hitler Rise To Power- Alex Gendler And Anthony Hazard (mp4)
- L5 How Hitler Became Chancellor In 1933 (pdf)
- L2 The German Revolution (pdf)
- L4 Adolf Hitler Timeline (docx)
- L4 Reasons Why The Nazi Party Grew In Popularity 1929-32 (docx)
- L2 Impact Of Wwi On Germany Diagram (pptx)
- L4 Growth Of Nazi Party Popularity Wall Information (docx)
- L2 Impact Of Wwi On Germany Diagram (pdf)
- L5 Failure Of The Weimar Republic (pptx)
- L2 Invasion Of The Ruhr (mp4)
- L4 How Hitler Became Chancellor In 1933 (doc)
- L9 Nazi Germany The Nazis And The Church Restistance To Hitler (mp4)
- L2 Homework 1 (docx)
- L2 German Revolution Info Hunt Posters (pdf)
- L4 Role Of Hitler And The Nazi Party (pptx)
- L8 Life In Nazi Germany (pptx)
- L7 Nazi Germany Economy (pptx)
- L9 Nazi Control And Dictatorship (pptx)
- L2 Impact Of The Treaty Of Versailles (docx)
- L2 German Revolution Info Hunt Posters (docx)
- L1 Wilhelmine Germany (pdf)
- L3 Weimar Germany (pptx)
- L2 Impact Of Wwi (pptx)
- L2 Hyperinflation In Germany (mp4)
- L1 Wilhelmine Germany (doc)
- AQA GCSE History Exam Booklets (2020 & 2021 Syllabus) (zip)