Download The Homestead Act of 1862 Worksheets
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be able to teach The Homestead Act of 1862 to your students?
Our worksheet bundle includes a fact file and printable worksheets and student activities. Perfect for both the classroom and homeschooling!
Table of Contents
Add a header to begin generating the table of contents
Summary
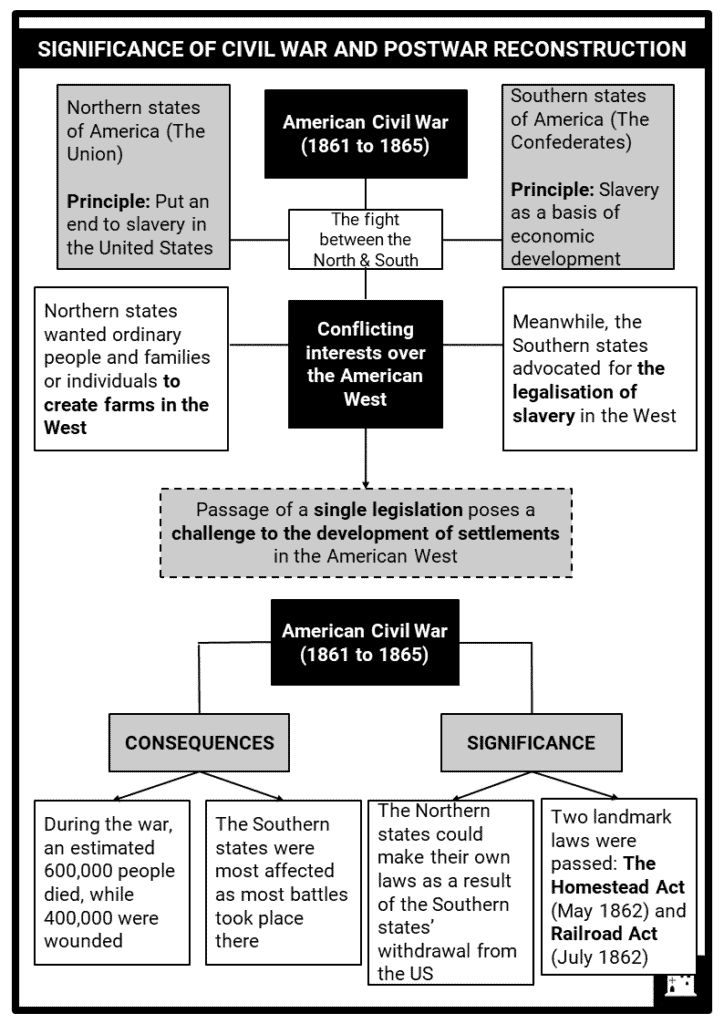
- Significance of the Civil War and postwar reconstruction
- Reasons for passing the Homestead Act of 1862
- Key features and significance of the Homestead Act of 1862
- The impacts of the Homestead Act of 1862
Key Facts And Information
Overview
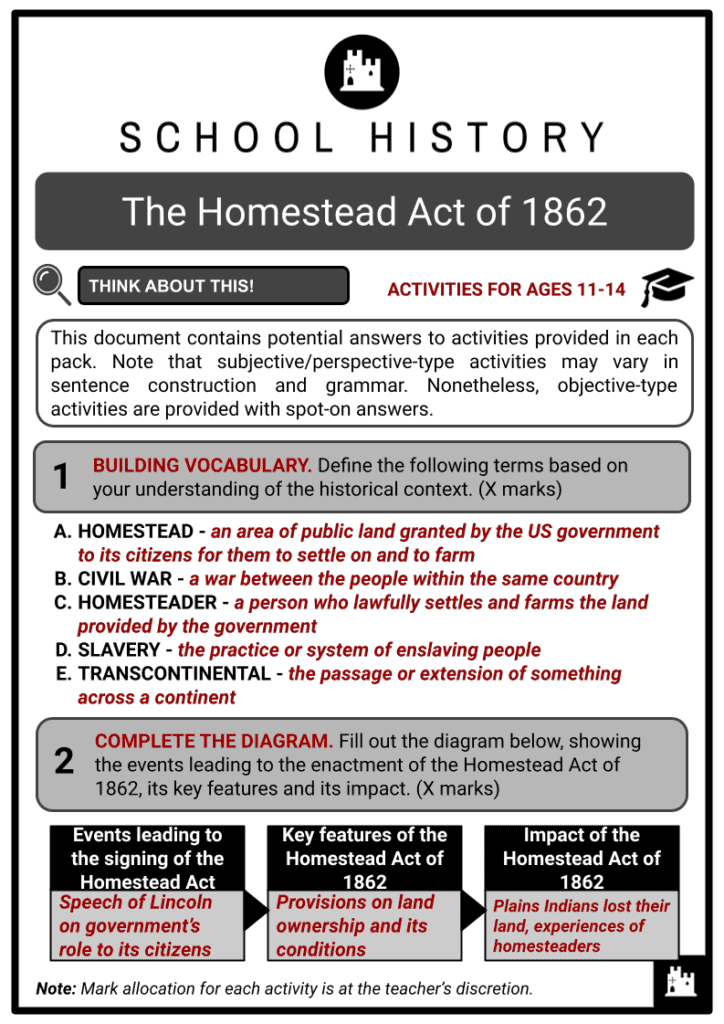
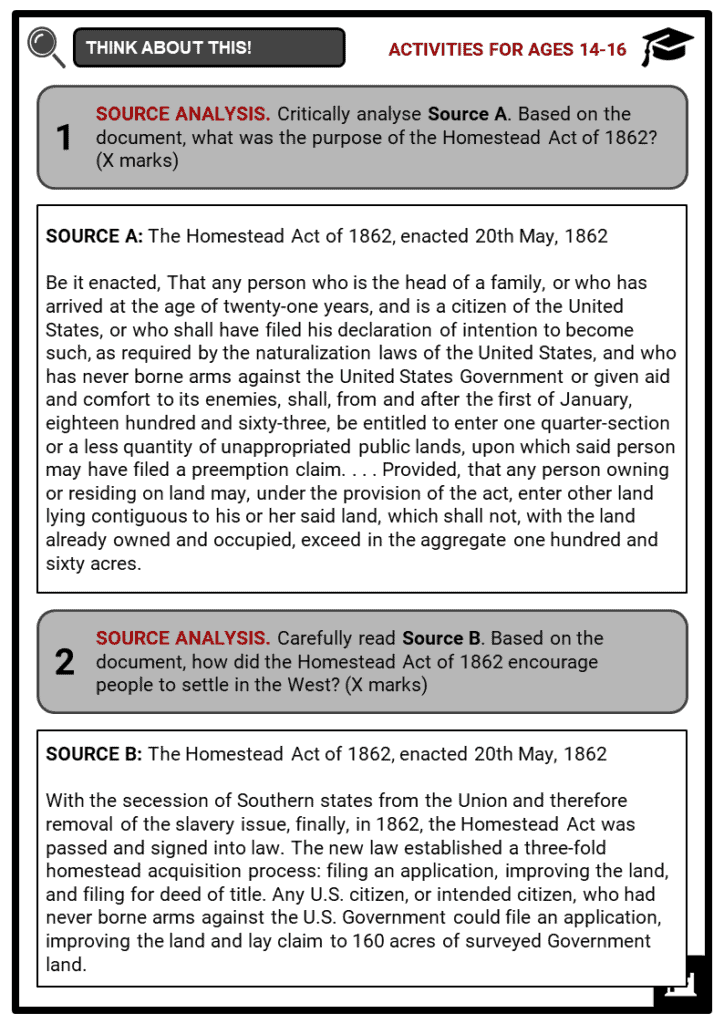
- The Homestead Act of 1862 was signed by US President Abraham Lincoln on the 20th of May, 1862. It granted African-Americans a 160-acre plot of public land for a small filing fee. Formerly enslaved, women, and even immigrants were allowed to become landowners as a result of this landmark legislation. It also promoted settlement, as well as development of the American West. A total of almost 270 million acres (109 million hectares) of land were distributed under this law.
Reasons For Passing The Homestead Act
- LINCOLN’S PRONOUNCEMENT: In a speech, US President Abraham Lincoln highlighted the government’s desire to improve human conditions, easing their burdens, and giving fair chances to people from all walks of life.
- THE PRESIDENT’S MESSAGE IN OHIO: Prior to his July 1861 speech, President Lincoln said that the passage of the [Homestead] act was a “worthy consideration” since people would have the opportunity to benefit from it.
Key Features And Significance Of The Homestead Act
- Before the Homestead Act of 1862 was implemented, land in the West cost around one dollar ($1) per acre. For ordinary families, this was still very expensive. When the act was passed in Congress in May 1862, it provided families with a different mechanism for them to afford land.
- FEATURES
- It allowed families to buy 160 acres of land (known as homesteads) for $10 on the condition that it would be used to build a home and establish a farm.
- AIMS
- It aimed to convince migrants to settle in the West so that land would not be owned primarily by the rich, and more taxes could be collected from smaller farms owned by many families.
- MECHANISMS
- If a person was older than 21 years, they could file a claim (also called buying a homestead) and work on the land on their own. The Act did not include the Plains Indians.
- Based on the law passed, the process was this: an individual would file an application, then he/she improves the land, and files for the patent. However, Native Americans lost much of their land because of this law.
- Significance of the Homestead Act of 1862
- The Homestead Act was successful in terms of the number of people who claimed land, migrated and permanently settled in the Great Plains. By 1876, more than six million acres of land were claimed.
- Despite its success, the Act had its pitfalls. For example, even if more land was claimed, 60% of the homesteads did not meet the conditions set out by the Act due to poor farming conditions in the Plains.
- In addition, some landowners veered away from the aims of the Act. They either sold their claims to others for profit or filed claims and were forced to turn it over to rich landowners, which was clearly a violation of the Homestead Act.
The Impact Of The Homestead Act Of 1862
- DEVELOPMENT OF SETTLEMENTS IN THE WEST: The Homestead Act of 1862 further opened up the West to more settlement and development, which resulted in a greater increase in agricultural activities, as well as the discovery and exploitation of natural resources. Furthermore, development of towns and job creation also attracted people to settle in the region.
- THE RISE OF TRANSCONTINENTAL RAILROAD: At the time the Act was receiving Presidential assent, the transcontinental railroad received Congressional approval. It also enabled further settlements in the West by easing transportation of people and goods to the region by replacing caravans, wagons and other forms of long-distance travelling options.
- INTENSIFYING WARS IN THE REGION: The Act had a negative impact on the Plains Indians and it further intensified wars between them and the white settlers in the region. Also, not all the land in the West was conducive for farming, which resulted in hunger and abandonment of land by Homesteaders during the early implementation of the law.