Teach any Edexcel IGCSE module : Dictatorship and conflict in the USSR, 1924–53, no prep needed!
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be fully prepared to teach any Edexcel iGCSE topic?
Every Edexcel iGCSE topic is covered, and each module comes complete with:
Dictatorship and conflict in the USSR, 1924–53
For this history module, students need to learn about:
The leadership struggle, 1924-29
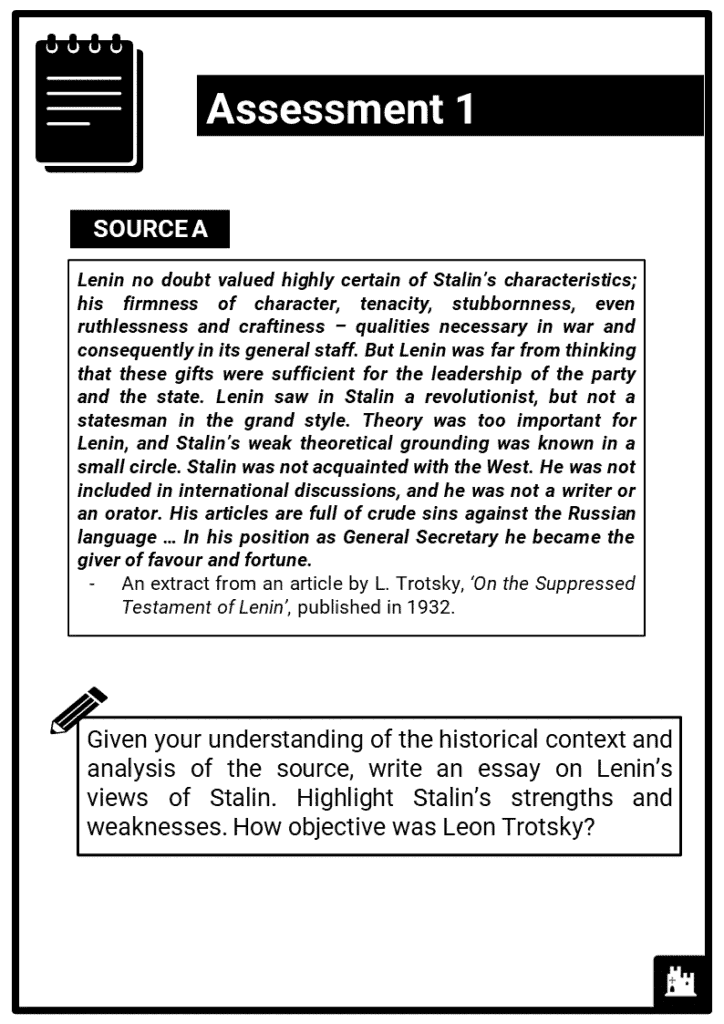
- The rivals for the leadership, including Stalin, Trotsky, Kamenev, Bukharin and Zinoviev;
- Strengths and weaknesses of Stalin and Trotsky;
- Stalin’s steps to power (1924–29), his emergence as the leader of the USSR and the reasons for his success.
Five-year Plans and collectivisation
- Stalin’s economic aims;
- Reasons for industrialisation, including the failings of the NEP;
- The nature of industrialisation, including Gosplan, the first three Five-year Plans, Stakhanovites;
- Success and failures of industrialisation;
- Reasons for and nature of collectivisation (1928);
- Kolkhoz and Motor TractorStations;
- Opposition of and removal of kulaks;
- Success and failures of collectivisation, including the Great Famine (1932–33).
Purges and show trials, the cult of Stalin and the revision of history
- Reasons for purges including the murder of Kirov;
- Key features of the purges of the 1930s;
- Control of the populace, including the roles of Yezhov, the NKVD and the gulags;
- The conditions in the gulags;
- Reasons for and features of the Moscow Show Trials (1936–38);
- Purges of the armed forces;
- Impact of the purges on the Soviet Union;
- Reasons for and methods of the cult of personality;
- Censorship, propaganda, ‘socialist realism’, control of education and the Soviet interpretation of history.
Life in the Soviet Union, 1924-41
- Effects of Stalin’s policies on living and working conditions in town and countryside;
- The differing experiences of social groups;
- Changes in family life and employment and in the political position of women;
- Changes in education;
- Reasons for, and features of, the persecution of ethnic minorities.
The Second World War and after, 1941-53
- The reasons for and extent of Soviet setbacks (1941–42), and the reasons for the survival of the USSR and success in driving back the German invasion, including war production;
- The significance of Stalingrad;
- Post-war recovery and the Fourth Five-year Plan;
- Stalin’s popularity;
- Post-war purges;
- The strength of the USSR on the death of Stalin in 1953 and the impact of his period in power.