Teach any Eduqas module 1G: Germany in Transition, 1919-1939, no prep needed!
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be fully prepared to teach any Eduqas GCSE topic 1G?
Every Eduqas topic 1G is covered, and each module comes complete with:
1G Eduqas GCSE History Component 1: Studies in Depth
Written examinations: 2 hours (comprising two papers of 1 hour duration each)
50% of qualification 100 marks (plus 6 marks for spelling, punctuation and grammar and use of specialist terms)
Learners study two Studies in Depth, one British and one non-British, from eight options in total. This component focuses study on substantial and coherent short time scales. Studies in Depth will provide learners with the opportunity to study history in greater depth and consequently understand the complexity of a society or historical situation more effectively.
Studies in Depth will focus study on different historical eras and different geographical contexts. This component encourages learners to use a wide range of historical sources. Learners should also study different historical interpretations of specific events and issues.
The two options studied must be from different historical eras (Medieval, 500-1500; Early Modern, 1450-1750; and Modern, 1700-present).
This module is from the Modern Era.
Curriculum for 1G. Germany in transition, 1919 to 1939
- This option focuses in depth on selected themes and issues relating to the history of Germany from 1919-1939. It includes the impact of WWI on Germany; the rise and fall of the Weimar Republic; conditions enabling the rise of the Nazi party and its consolidation of power; the impact of Nazi policies on life in Germany for both Germans and minorities; and the use of propaganda, terror and persuasion to achieve its ideological goals.
- Candidates will be required to consider the main drivers for the emergence of the Nazi party and develop an awareness of how aspects of German life during this period have been represented and interpreted through different lenses to contribute to the wider historical debate about the period.
- Students should be able to address the key questions in each topic area using a range of historical sources and with well-reasoned arguments based on the historical context.
- Each of the modules address required content for the Eduqas assessment (in italics below).
- This option cannot be studied alongside Component 2, option 2B: The Development of Germany, 1919-1991.
Key Questions and Required Content
Impact of the First World War
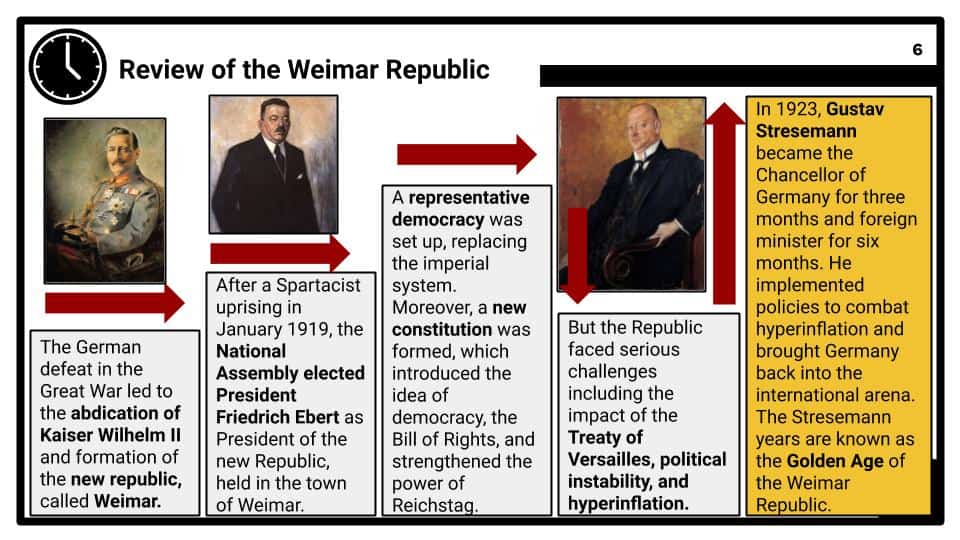
What challenges were faced by the Weimar Republic from 1919-1923?
Required content: Impact of Versailles; weaknesses of Weimar government; political instability – Spartacist, Kapp, Munich Putsches; hyperinflation; events in the Ruhr 1923.
The Recovery of Weimar
Why were the Stresemann years considered a ‘golden age’?
Required content: Recovery from hyperinflation; Dawes and Young Plans; Locarno Pact; League of Nations; U.S. investment; social and political developments.
End of the Weimar Republic
How and why did the Weimar Republic collapse between 1929 and 1933?
Required content: Social and political impact of the Depression on the Weimar Republic; Hitler’s electoral appeal; the role of the SA; propaganda; political extremism and scheming 1929-1932
Consolidation of Power
How did the Nazis consolidate their power between 1933 and 1934?
Required content: Hitler as Chancellor; Reichstag Fire; 1933 election and Enabling Act; trade unions and political parties; Night of the Long Knives; Hitler becomes Führer.
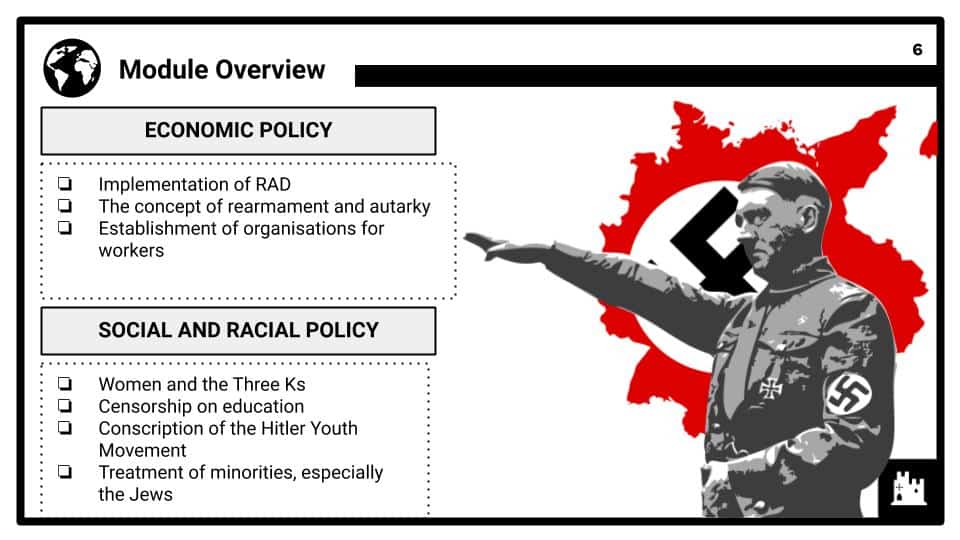
Nazi Economic, Social and Racial Policy
How did the Nazi economic, social and racial policies affect life in Germany?
Required content: Reducing unemployment; policy towards workers; women and the Three Ks; controlling education; the Hitler Youth Movement; treatment of the Jews.
Terror and Persuasion
What methods did the Nazis use to control Germany?
Required content: Use of the SS and Gestapo; control of the legal system; Goebbels and propaganda; use of rallies, radio and cinema; censorship of newspapers and the arts.
Hitler’s foreign policy
What factors led to the outbreak of war in 1939?
Required content: Hitler’s foreign policy aims; rearmament and conscription; the Rhineland 1936; Anschluss 1938; Sudetenland 1938; Nazi-Soviet pact 1939.