Teach any Edexcel IGCSE module : South Africa: from Union to the end of apartheid, 1948–94, no prep needed!
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be fully prepared to teach any Edexcel iGCSE topic?
Every Edexcel iGCSE topic is covered, and each module comes complete with:
Paper 1: Depth Studies, South Africa, from union to the end of apartheid, 1948-94
What students need to learn:
- Setting up apartheid, 1948–54
- Nature and extent of segregation in 1948. Election of 1948 and reasons for Nationalist victory. Origins and nature of apartheid and its development to 1954, including Population Registration Act (1950), prohibitions on mixed marriages, Group Areas Act (1950), Pass System and creation of Reserves, Separate Amenities Act (1953), Bantu Education Act (1953). Opposition and resistance to the Nationalist Government and the suppression of it (1948–1954).
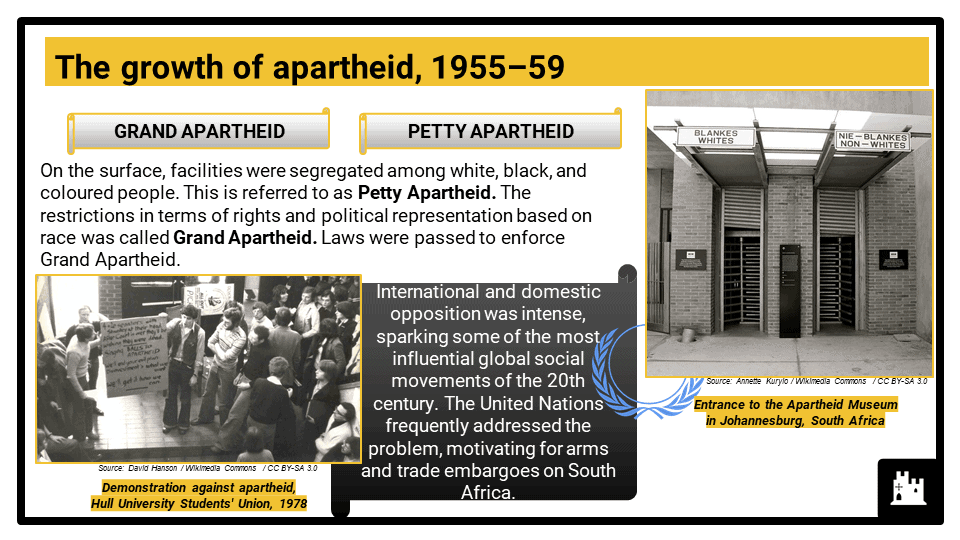
- The growth of apartheid, 1955–59
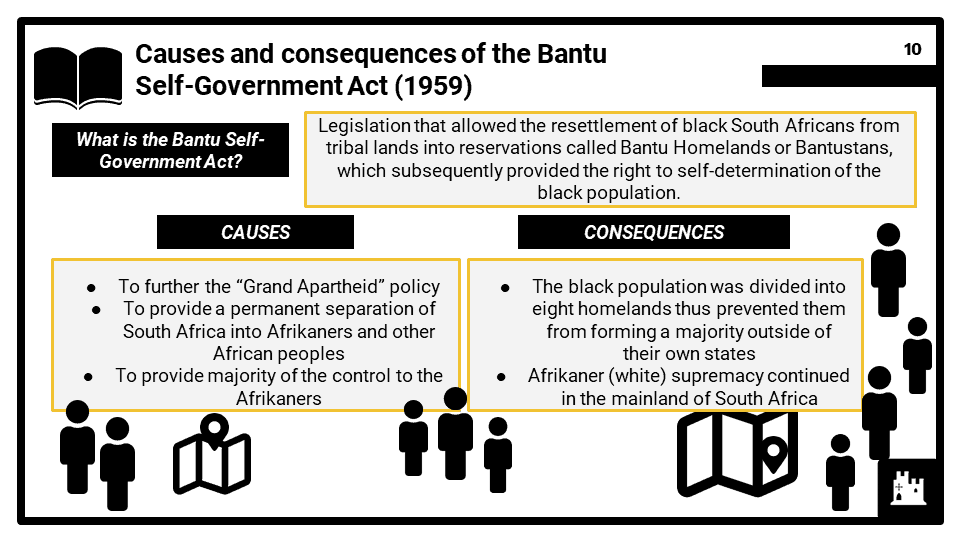
- Petty apartheid and the impact of segregation and changes to education. Development of apartheid under Verwoerd and Vorster, including causes and consequences of the Bantu Self-Government Act (1959).
- Resisting apartheid, 1955–78
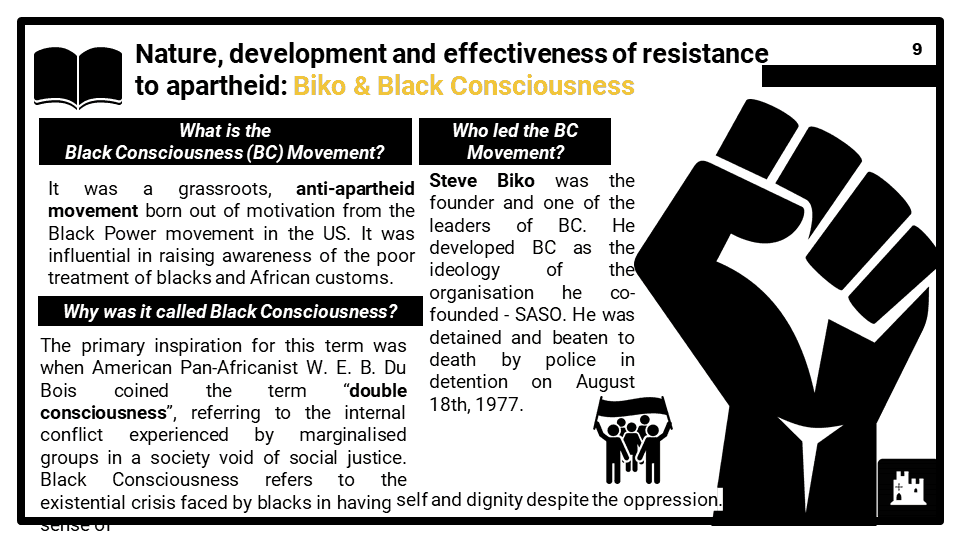
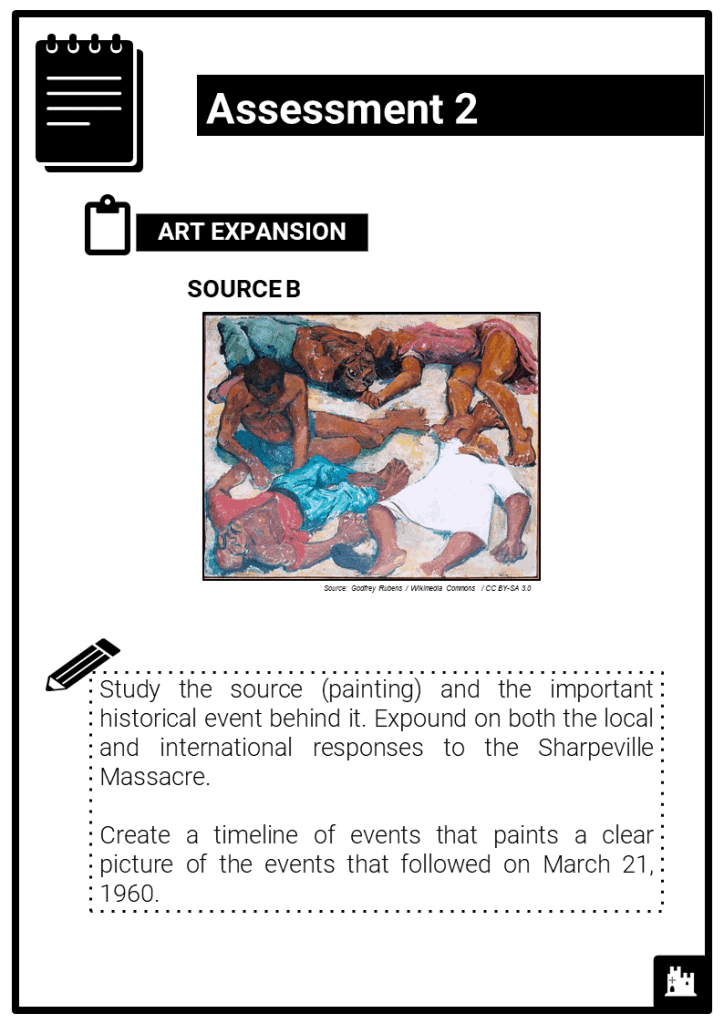
- Nature, development and effectiveness of resistance to apartheid, including Nelson Mandela, ANC, Biko and Black Consciousness. Other forms of civil disobedience, including anti-pass law demonstrations, Sharpeville (1960), Spear of the Nation (1961) and Soweto (1976) and their consequences. Enforcement of apartheid, including the Treason Trials (1956–61). Extent of threats to apartheid by 1978, including the international reaction.
- PW Botha – response to resistance, 1978–90
- Nature and development of opposition in this period, the United Democratic Front, ANC, Township Unrest, Church leaders, and Botha’s response. Reasons for the reforms of PW Botha and their consequences for National Party and White, Black and Coloured South Africans. Afrikaaner resistance to reforms, especially the work of the AWB. Reasons for and consequences of the State of Emergency (1985–1990). International opposition to apartheid and the impact of boycotts and sanctions.
- Dismantling Apartheid, 1990–94
- Reasons for the reforms of FW de Klerk and their consequences for the repeal of apartheid (1991). Importance of de Klerk, Nelson Mandela and other individuals in bringing about end of apartheid. Mandela, ANC and the multiracial Election of 1994.