Download The Events of World War 2
Click the button below to download this worksheet for use in the classroom or at home.
Download →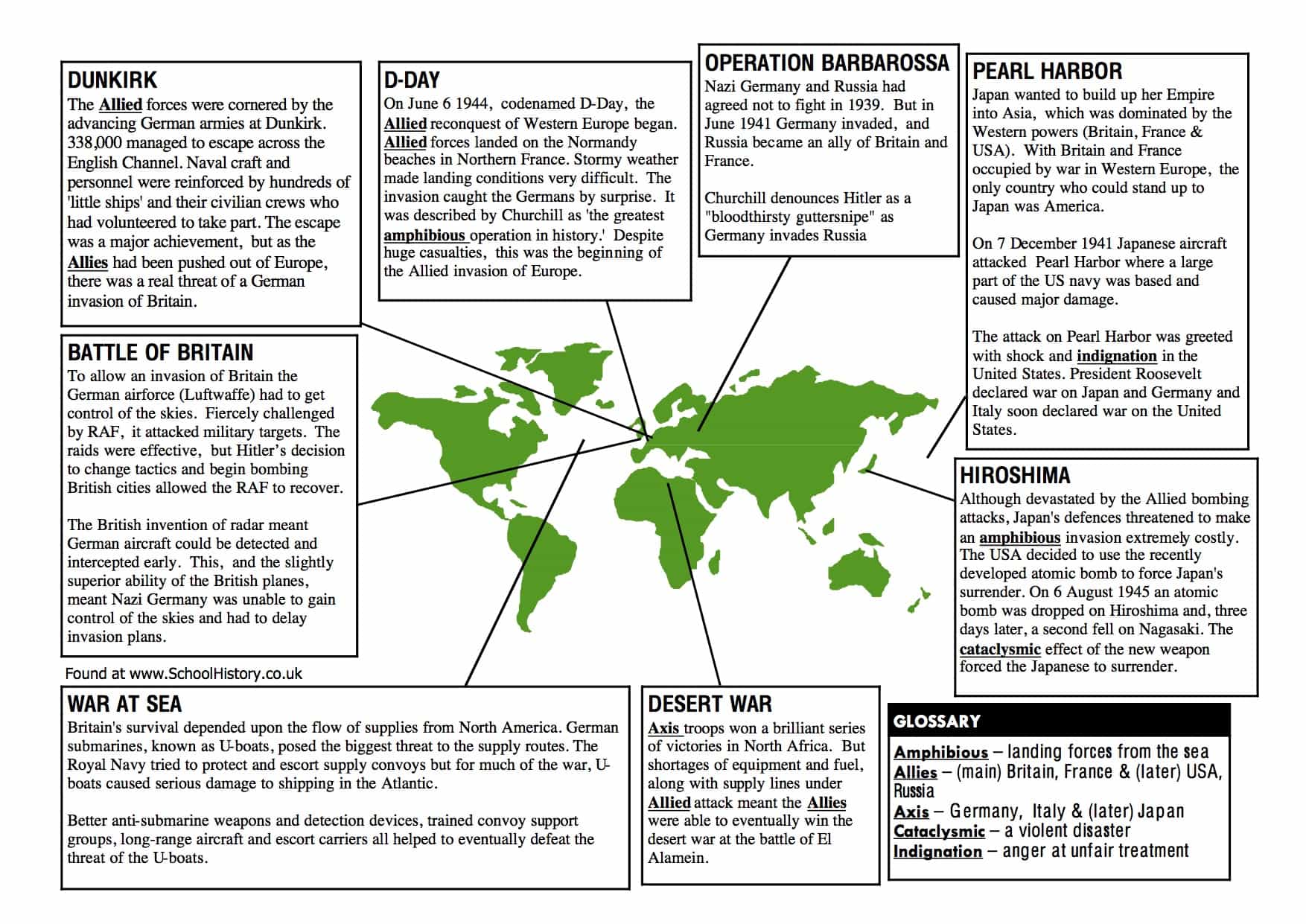
DUNKIRK
The Allied forces were cornered by the advancing German armies at Dunkirk. 338,000 managed to escape across the English Channel. Naval craft and personnel were reinforced by hundreds of ‘little ships’ and their civilian crews who had volunteered to take part. The escape was a major achievement, but as the Allies had been pushed out of Europe, there was a real threat of a German invasion of Britain.
BATTLE OF BRITAIN
To allow an invasion of Britain the German airforce (Luftwaffe) had to get control of the skies. Fiercely challenged by RAF, it attacked military targets. The raids were effective, but Hitler’s decision to change tactics and begin bombing British cities allowed the RAF to recover.
The British invention of radar meant German aircraft could be detected and intercepted early. This, and the slightly superior ability of the British planes, meant Nazi Germany was unable to gain control of the skies and had to delay invasion plans.
WAR AT SEA
Britain’s survival depended upon the flow of supplies from North America. German submarines, known as U-boats, posed the biggest threat to the supply routes. The Royal Navy tried to protect and escort supply convoys but for much of the war, U- boats caused serious damage to shipping in the Atlantic.
Better anti-submarine weapons and detection devices, trained convoy support groups, long-range aircraft and escort carriers all helped to eventually defeat the threat of the U-boats.
DESERT WAR
Axis troops won a brilliant series of victories in North Africa. But shortages of equipment and fuel, along with supply lines under Allied attack meant the Allies were able to eventually win the desert war at the battle of El Alamein.
PEARL HARBOR
Japan wanted to build up her Empire into Asia, which was dominated by the Western powers (Britain, France & USA). With Britain and France occupied by war in Western Europe, the only country who could stand up to Japan was America.
On 7 December 1941 Japanese aircraft attacked Pearl Harbor where a large part of the US navy was based and caused major damage.
The attack on Pearl Harbor was greeted with shock and indignation in the United States. President Roosevelt declared war on Japan and Germany and Italy soon declared war on the United States.
HIROSHIMA
Although devastated by the Allied bombing attacks, Japan’s defences threatened to make an amphibious invasion extremely costly. The USA decided to use the recently developed atomic bomb to force Japan’s surrender. On 6 August 1945 an atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima and, three days later, a second fell on Nagasaki. The
cataclysmic effect of the new weapon forced the Japanese to surrender.
PDF Worksheet:
-
- Aimed at Students studying at UK Year 7,8,9 or equivalent
- Free to download
- Use as you wish in the classroom or home environment
- Structured study guide and challenging questions.
