Teach any WJEC module : Radicalism and Protest, 1810-1848, no prep needed!
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be fully prepared to teach any WJEC GCSE topic?
Every WJEC topic is covered, and each module comes complete with:
WJEC GCSE History Component 1: Studies in Depth
Written examination: 1 hour 25% of qualification 50 marks (plus 3 marks for spelling, punctuation and grammar and the use of specialist language)
Learners study one Study in Depth from four options in total. This unit focuses study on a substantial and coherent short time scale in the history of Wales within Britain. This unit will provide learners with the opportunity to understand the complexity of a society in the history of Wales within Britain more effectively. Learners should understand how the experience of people within Wales can be distinctive but also that it can reflect the wider relationship with Britain. This unit encourages learners to use a wide range of historical sources. Learners will also study different historical interpretations of specific events and issues.
Unit 1: Studies in Depth
Sub-section: Wales and the wider perspective
Module: 1B Radicalism and Protest, 1810-1848
This option focuses in-depth on selected themes and issues relating to the history of radicalism and protest during the period 1810-1848. Learners will be required to consider the impact of the growth of radicalism, 1810-1822, the importance of industrial protest with a particular focus on events in industrial Wales, and the nature of rural protest in this period. Learners should understand how the experience of people within Wales at this time was distinctive but also that this can reflect the wider relationship with Britain. Learners should develop an awareness of how aspects of life in this period have been represented and interpreted and they should also address the key questions in each topic area using a range of historical sources. Where appropriate, these will contain material from Welsh sources. The required content below shows which key features and characteristics of the period must be studied.
Key Questions and Required Content
- The impact of the French Revolution and Napoleonic Wars What were the main pressures facing the country c.1810?
- The influence of the Corresponding Societies; the impact of war on the economy; demobilised soldiers; the Corn Laws; the demand for parliamentary reform; the impact of industrialisation on radical thinking.
- Early outbreaks of protest What were the most significant protests in the period 1810-1832?
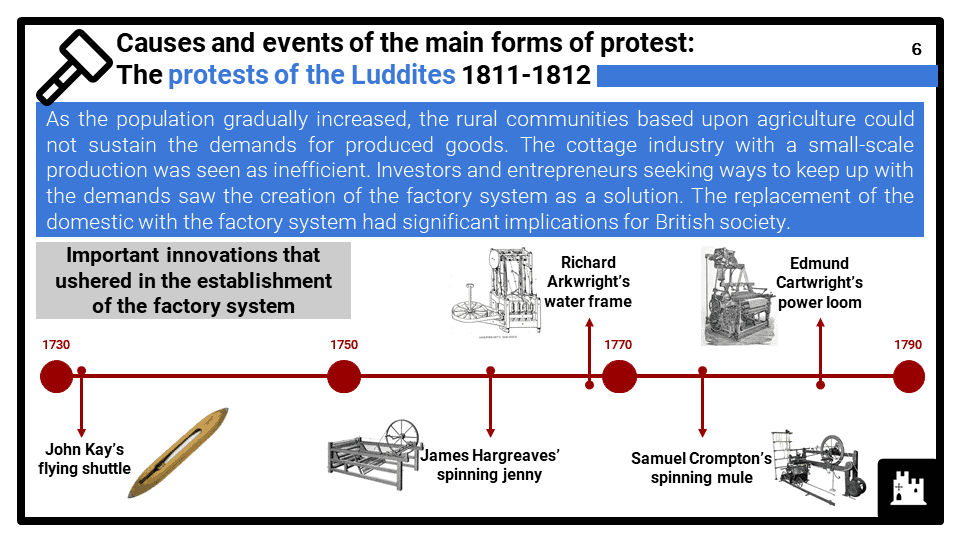
- Causes and events of the main forms of protest including: the protests of the Luddites 1811-1812; the Spa Fields Riots, 1816; the march of the Blanketeers, 1817; the forming of political unions; the Reform Bill Riots, 1831.
- Government reaction: How did the government react to popular protest at this time?
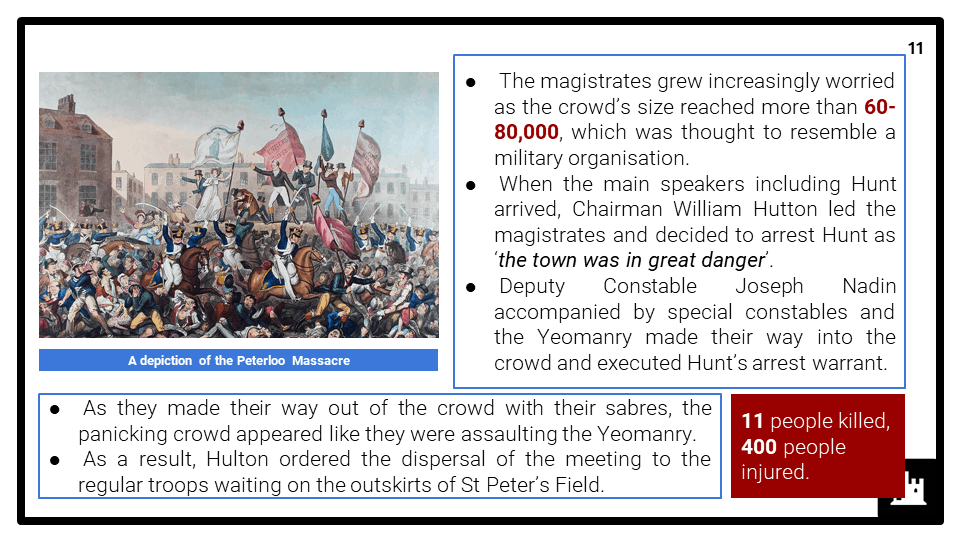
- Agent provocateurs; the suspension of habeas corpus,1817; the Peterloo Massacre,1819; the Six Acts; the Cato Street Conspiracy,1820; the 1832 Reform Act.
- Industrial protest in Wales Why did the Merthyr Rising break out in 1831?
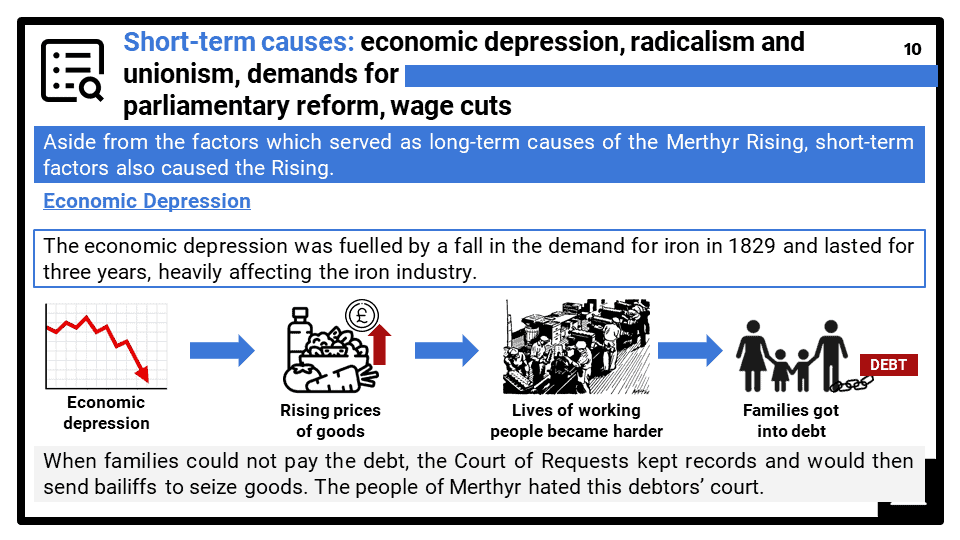
- Long-term causes: working and living conditions, the truck system, the role of the industrialists; short-term causes: economic depression, radicalism and unionism, demands for parliamentary reform, wage cuts; the events of the Merthyr rising.
- The growth of Chartism: How and why did Chartism develop?
- The reasons for the rise of Chartism; the roles of Lovett and O'Connor; physical and moral force Chartism; the Convention and the Petitions; Chartism in Wales: the march on Newport and events at Llanidloes, 1839.
- Rural protest: What conditions led to rural protests in this period?
- The causes of the Swing Riots; the activities of the Swing rioters: destruction of property, threatening letters; the causes of the Rebecca Riots; the activities of the Rebecca Rioters: threats, attacks on tollgates and workhouses.
- Impact of industrial and rural protest: What were the results of the industrial and rural protests after 1830?
- The results of the Merthyr Rising: the execution of Dic Penderyn; abolition of the truck system, parliamentary representation; reasons for the failure of the Chartist movement; government reaction to rural protest: arrests, transportation, and legislation including the Poor Law Amendment Act, 1834, and the Turnpike Act, 1844.
This module download also includes the following teaching resources:
- Module 2 Bbc Criminal Histories The Nottingham Riots (mp4)
- Module 2 Consequences Of The Spa Field Riots (pdf)
- Module 1 Thomas Paine Information (pdf)
- Module 5 The Chartist Movement (mp4)
- Module 2 Horrible Histories- Georgian Luddites Heavy Metal Song (mp4)
- Module 2 March Of The Blanketeers (docx)
- Module 6 Swing Riot Information (pdf)
- Module 5 Chartism (pdf)
- Module 2 March Of The Blanketeers (pdf)
- Module 3 16th August 1819- Protesters Killed In The Peterloo Massacre In Manchester (mp4)
- Module 6 Stop Look Listen- Tales From Wales The Rebecca Riots Excerpt 2001 (mp4)
- Module 3 British Reform Bill Of 1832 Video (mp4)
- Module 7 Impact Of Industrial And Rural Protest (pdf)
- Module 2 Consequences Of The Spa Field Riots (docx)
- Module 2 Early Outbreaks Of Protest (pptx)
- Module 1 The French Revolution -in A Nutshell (mp4)
- Module 4 Merthyr Uprising And Dic Penderyn (mp4)
- Module 6 Swing Riot Information (docx)
- Module 2 Radicalmovie (mp4)
- Module 7 Impact Of Industrial And Rural Protest (docx)
- Module 3 Government Reaction To Protest Work Booklet (docx)
- Module 6 Rural Protest (pptx)
- Module 1 Thomas Paine Information (docx)
- Module 5 Newport Rising 1839 (mp4)
- Module 5 Chartism (docx)
- Module 1 Impact Of The French Revolution And Napoleonic Wars (pptx)
- Module 3 Government Reaction To Protest Work Booklet (pdf)
- Module 4 Industrial Protest In Wales (pptx)
- WJEC_Eduqas Exam Booklets (zip)