Teach any Edexcel IGCSE module B1: America: from new nation to divided union, 1783–1877, no prep needed!
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be fully prepared to teach any Edexcel iGCSE topic B1?
Every Edexcel iGCSE topic B1 is covered, and each module comes complete with:
Paper 2: Breadth Studies, America, from new to divided union, 1783-1877
What students need to learn:
- Building a new nation, 1783–1809
- The nature and impact of tensions between large and small states and the clash over slavery. The significance of Shays’ Rebellion. The Connecticut Compromise and the Constitutional Convention (1787). The work of, and divisions between, the Founding Fathers, including Federalists versus Anti-federalists, the Bill of Rights. Strict Constructionists versus Loose Constructionists. Jefferson’s presidency, including his ‘1800 Revolution’ and States’ Rights.
- Westward expansion and Native American removal, 1803–49
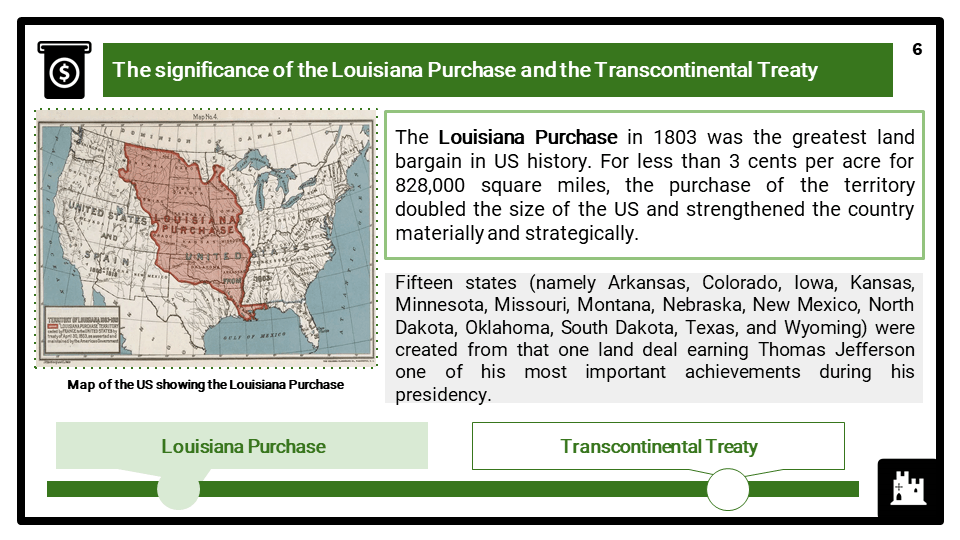
- Opposition to Westward expansion from Spain, Britain, Mexico and Native Americans. The significance of the Louisiana Purchase and the Transcontinental Treaty and the annexation of Texas. Expansion and sectional conflict – the Missouri Compromise. The Indian Removal Act, the Trail of Tears. Settling the West – Manifest Destiny, migration to Texas and Oregon and the significance of the California Gold Rush.
- Slavery, the South and the causes of secession, 1850–61
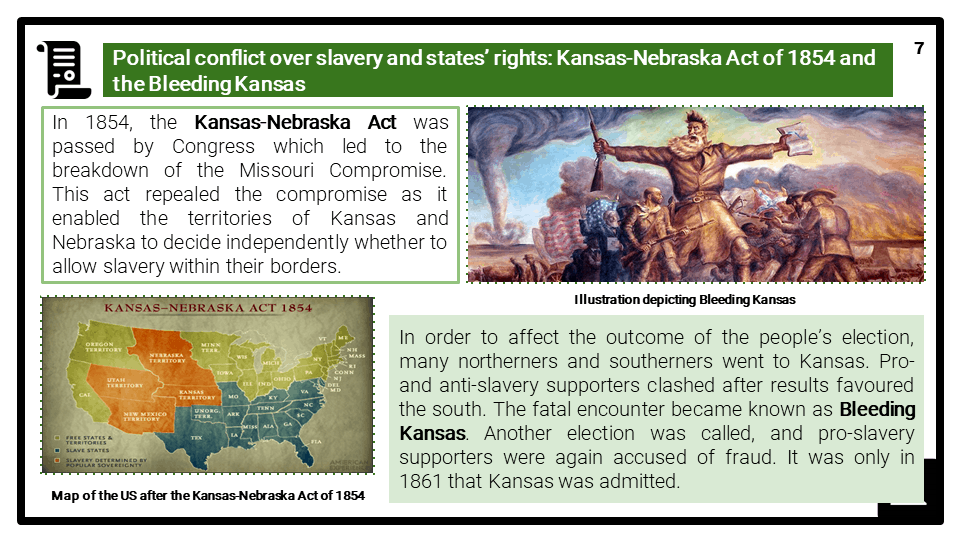
- The political conflict over slavery and states’ rights, including the compromise of 1850, the Kansas– Nebraska Act of 1854 and Bleeding Kansas and the Dred Scott case. The economic origins of the division between Union and Confederacy. The immediate causes of the Civil War, including the roles of John Brown, Abraham Lincoln, Fort Sumter and the secession of South Carolina.
- Civil War and the end of slavery, 1861–65
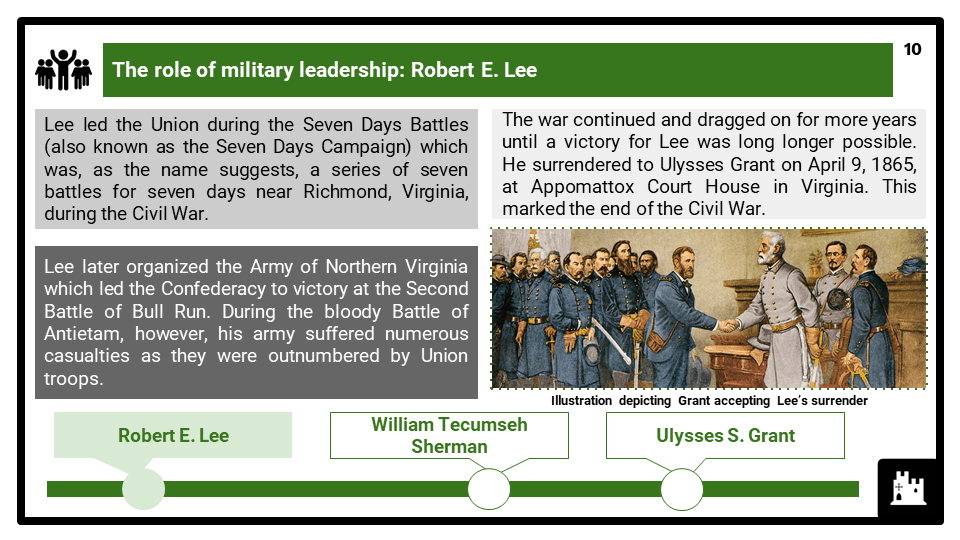
- The Civil War and the reasons for Union victory. The role of military leadership, including Lee, Sherman and Grant. The Union naval blockade. The impact of the political leadership of Lincoln and Davis; the Emancipation Proclamation and Gettysburg Address. The impact of the Battles of Gettysburg and Vicksburg (1863) and the ‘March Through Georgia’ (1864). The consequences of the destruction of the Southern economy.
- A More Perfect Union? 1865–77
- The role of Johnson and the Reconstruction Act of 1867 restoring the seceded states to the Union. Black Reconstruction: the Freedman’s Bureau and the Southern response, the Black Codes; the Civil Rights Acts of 1866 and 1875 and the 13th, 14th and 15th Amendments. The failure of Grant’s Peace Policy towards Native Americans, Custer’s Last Stand and its aftermath.