Teach any Edexcel IGCSE module B8: Diversity, rights and equality in Britain, 1914-2010, no prep needed!
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be fully prepared to teach any Edexcel iGCSE topic B6?
Every Edexcel iGCSE topic B6 is covered, and each module comes complete with:
Paper 2: Breadth Studies, Diversity, rights and equality in Britain, 1914-2010
What students need to learn:
- The fight for recognition, 1914-1928
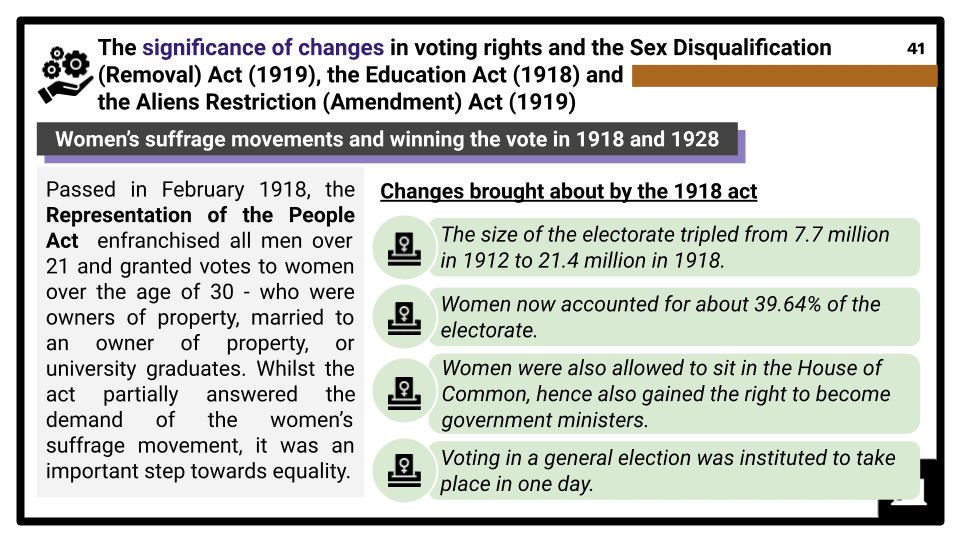
- The nature of diversity, rights and equality in Britain in 1914, including attitudes to race, gender, disability and class, and pressures for change. The impact of the First World War on attitudes to, and opportunities for, women, ethnic minorities, the working classes and disabled people, including treatment for mental and physical disability. The significance of changes in voting rights and the Sex Disqualification (Removal) Act (1919), the Education Act (1918) and the Aliens Restriction (Amendment) Act (1919).
- The impact of Depression and war, 1928-45
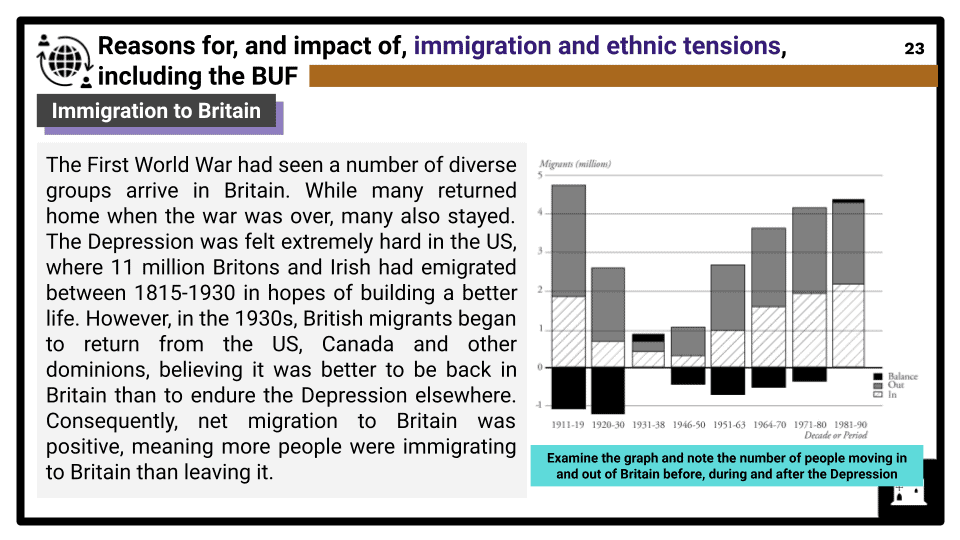
- Race, gender, disability and class in Depression and war, including eugenics. The impact of unemployment and the Jarrow Crusade. Reasons for, and impact of, immigration and ethnic tensions, including the BUF. Changing experiences in the Second World War, including the introduction of national service, the treatment of aliens, the ‘colour bar’ and the significance of the case of Learie Constantine and the Imperial Hotel. The significance of the Disabled Persons (Employment) Act (1944).
- Consequences of war and the end of empire, 1944-62
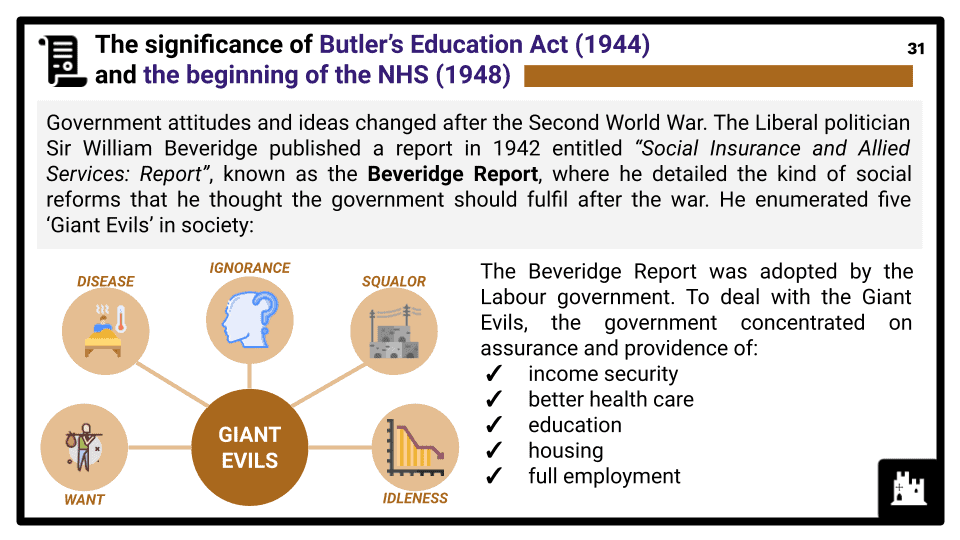
- The contribution and treatment of Empire and Commonwealth immigrants, including the Windrush, African and South Asian immigrants. Claudia Jones and the Caribbean Carnival. Barriers to change, including the significance of the Commonwealth Immigrants Act (1962). Reasons for changes in attitudes to, and opportunities for, women, sexual minorities and disabled people, including Sir Ludwig Guttmann and the Paralympic Games movement, and the Wolfenden Report (1957). The significance of Butler’s Education Act (1944) and the beginning of the NHS (1948).
- Changes in civil rights, c1962-1986
- The reasons for and extent of the social revolution in diversity, rights and equality - the impact of: feminism and the women’s strike at Dagenham; campaigns for racial equality and the Bristol Bus Boycott; comprehensive education and university grants; the Warnock Report (1978); improved rights for disabled people and sexual minorities. Barriers to change, including Enoch Powell, the anti-immigration movement, and the Immigration Act (1971). The significance of legislation in removing barriers: the Race Relations Act (1965); the Sexual Offences Act (1967); Chronically Sick and Disabled Persons Act (1970); Castle’s Equal Pay Act (1970); the Sex Discrimination Act (1975).
- Changes in opportunity and culture, 1986-2010
- The drive for equal rights and cultural diversity, including the impact of the National Council for Civil Liberties, the Stephen Lawrence case, third-wave feminism, the LGBT Foundation and the British Council of Organisations of Disabled People. The significance of diversity for the arts and culture in Britain. The significance of increased educational opportunities. Barriers to change, including religious intolerance, institutional racism, continuing sexism, Section 28 (1988), disability discrimination, continuing social and economic inequality. The significance of the Equality Act (2010).