Download Queen Victoria Worksheets
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be able to teach Queen Victoria to your students?
Our worksheet bundle includes a fact file and printable worksheets and student activities. Perfect for both the classroom and homeschooling!
Table of Contents
Add a header to begin generating the table of contents
Summary
- The Early Life of Queen Victoria
- Marriage to Prince Albert
- The Reign of Queen Victoria
- Death and Legacy
Key Facts And Information
Let’s find out more about Queen Victoria
- Queen Victoria’s reign was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom. It is known for being a reign of great cultural expansion, building of railways and the London Underground, and the advances in industry, science, and communications.
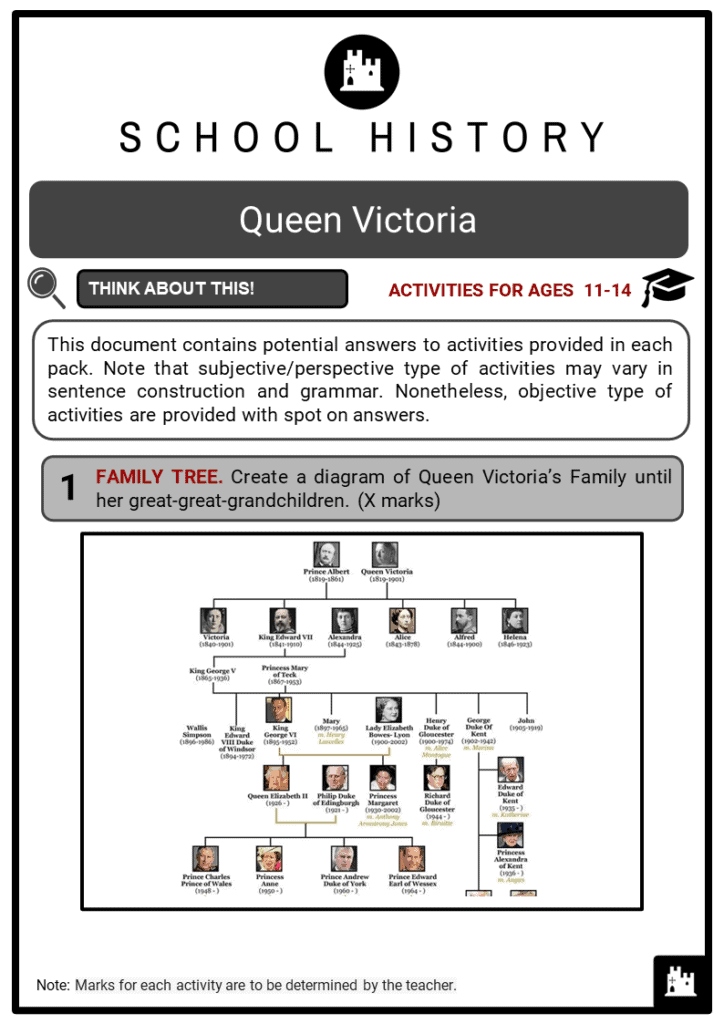
- The English monarchy took on its modern ceremonial character during her reign, by which Queen Victoria and Prince Albert had nine children, through whose marriages were descended many of the royal families of Europe.
Early Life
- Alexandrina Victoria was born on May 24, 1819 at Kensington Palace in London. Her father, Prince Edward, died when she was just 8 years old, and her mother, Princess Victoria, became a domineering influence in her life. Queen Victoria was described as a warm-hearted and lively child.
- Queen Victoria described her childhood as “rather melancholy.” She was educated at the Royal Palace by a governess. She had talent in drawing and painting and developed a passion for journal writing. Victoria was brought up with a strict set of rules and regulations known as the ‘Kensington System’. Throughout her childhood, she was closeted and controlled by her mother and her assistant John Conroy.
Marriage
- After Victoria was crowned as queen, she met many potential suitors from different Royal Houses across Europe. The Queen’s husband had to be a royal, Protestant, and at an appropriate age.
- Queen Victoria and Prince Albert first met when they were both 17.
- When they were 20, he returned to England, and since Victoria was in love with him, she proposed marriage since he can’t propose to the queen.
- The couple were married on Feb 10, 1840 in the Chapel Royal of St James's Palace, London.
- They had a very close, intimate relationship, and Queen Victoria would describe the intensity of feelings towards her husband.
- “MY DEAREST DEAREST DEAR Albert … his excessive love & affection gave me feelings of heavenly love & happiness I never could have hoped to have felt before!”
- In the same year, she gave birth to her first child named after her. Victoria and Albert had nine children in total though she found pregnancy and childbirth difficult.
- Victoria had traditional views in fulfilling the role of wife and mother, and even though she was a queen and Albert was prince consort, they equally shared government responsibilities.
Reign Of Queen Victoria
- Her grandfather George III died in 1830 and his successor King William IV also passed away in 1837. Thus, despite being fifth in line for the throne, the crown was passed onto the 18-year-old Victoria who was then unprepared for the title.
- One of Queen Victoria’s first moves was to become more independent and cut free from her mother and the controlling atmosphere.
- During the reign of Queen Victoria, the Great Britain experienced unprecedented expansion in industry, building railways, bridges, underground sewers and power distribution networks throughout much of the empire.
- The queen was emblematic at that time as an enthusiastic supporter of the British Empire and for her quote “The sun never sets on the British Empire”.
- The theory of evolution by Charles Darwin was one of the scientific advancements during the Victorian period.
- The technology also improved starting from the development of telegraph and popular press.
- Britain was also able to expand its imperial reach, encompassing Canada, Australia, India, and other lands in Africa and South Pacific. In 1877, Queen Victoria was made Empress of India, in a move instigated by the imperialist Disraeli.
- Queen Victoria was conservative with regards to her political and social views. Her opposition with women’s basic rights led to an unfortunate episode in her reign. However, this decline in support had been reversed when she was able to make Great Britain rise as the superpower of the era.
- The marriage of Victoria’s children played a great role in helping Great Britain avoid European entanglements, by which she became related to the royal houses of nearly every major European power.
- The English constitutional arrangement denied Victoria’s powers in foreign affairs, however, she was able to rule her family with an iron hand that helped keep the Great Britain away from the intrigues of European politics.
- The political atmosphere in British Parliament went through a major transition during her reign. Liberal and Conservative parties were formed from the Tory Party, and started a succession of opposing administration.
- Queen Victoria became the mediator between the arriving and departing prime ministers.
- There were seven assassination attempts made on Victoria’s life between 1840 and 1882. One was when she was still pregnant with her first child. Edward Oxford attempted to assassinate her while she was in a carriage with her husband.
Death And Legacy
- Queen Victoria faced her death that ended her reign in January 22, 1901. She already had written instructions regarding her funeral in 1897. Victoria wanted it to be not too black and asked for cheerful flowers. She was dressed in a white dress and her wedding veil. The queen was buried beside Prince Albert at Frogmore.
- Queen Victoria was the longest-reigning British monarch and the longest-reigning queen regnant in world history with a reign of 63 years, 7 months, and 2 days, until her great-great-granddaughter Elizabeth II surpassed her in 2015. Victoria managed to influence government policy and helped shape the culture of the Victorian era, though British sovereigns no longer wielded significant political power when she first sat on the throne.
- During the Victorian Era, the gradual establishment of a modern constitutional monarchy in Britain continued. The reforms of the voting system were able to increase the power of the House of Commons at the Expense of the House of Lords and the monarch.
- There are places and memorials dedicated to Queen Victoria all around the world such as the: Two Australian states Victoria and Queensland, Lake Victoria – Africa’s largest lake, Victoria Falls and the capital of the island nation of Seychelles. The Victoria Cross award was introduced in 1856 to reward the acts of valour during the Crimean war and remains the highest award for bravery. Victoria Day is a local public holiday in parts of Scotland and a Canadian statutory holiday celebrated before or on May 24.
Image sources:
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/de/Queen_Victoria_-_Winterhalter_1859.jpg
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/68/Duchess_of_Kent_and_Victoria_by_Henry_Bone.jpg/340px-Duchess_of_Kent_and_Victoria_by_Henry_Bone.jpg
- https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6d/Edward_Oxford%27s_assassination_attempt_on_Queen_Victoria%2C_G.H.Miles%2C_watercolor%2C_1840.jpg/400px-Edward_Oxford%27s_assassination_attempt_on_Queen_Victoria%2C_G.H.Miles%2C_watercolor%2C_1840.jpg